Shape a Sustainable & Scalable Business with Three Dots …
Strategy. Innovation. Marketing!
Strategy. Innovation. Marketing!
Set Your Business Position Right in the Market Mind to Achieve a Sustainable and Scalable Growth through a Unique Value Proposition.
Micro and Small Businesses are losing their market share in excessive competition in any segment. More competitors – less market share. Competitors bite off your clients. One of the tactics is the businesses scarify the price for competitive advantage. Businesses are pushed to the point when they are lowering the prices because the competitors are doing so, even if the product/service value is higher. In addition, the businesses think the marketing equals advertising, but most often they face with low return on marketing advertisement investment. On top of it, clients are exposed to similar products/services from different competitors and are curious to try.
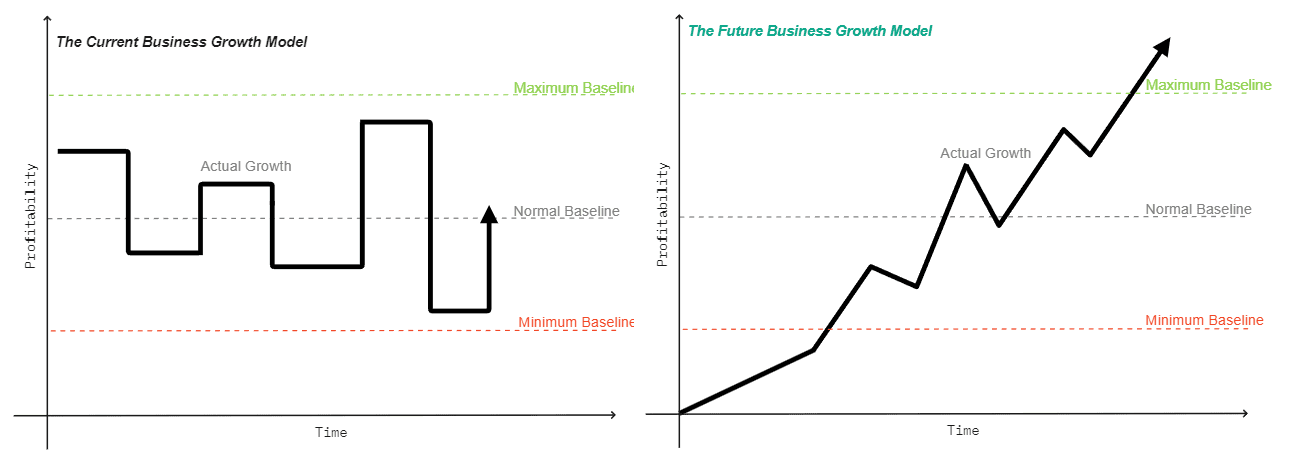
Most of the current businesses growth is similar to the rectangular pulse-shaping (getting one project or work order after another one) which is not sustainable & Scalable over the long run.
However, the fundamental question is How are Micro or Small businesses supposed to achieve a strategic goal in their market and then how to maintain the achievement and grow from there for a sustainable & Scalable business model that is both profitable and defendable to retain a profitable position in the market?
The short answer can be a Strategic Innovation that should be aligned with a Strategic Positioning in the market over a time to have a Sustainable & Scalable business growth that is both profitable and defendable.
Strategy, Innovation, Marketing & Operation are core members of a small business family. The businesses are mostly good at technical execution but mostly are inadequate or behind Strategy, Innovation & Marketing elements such as having a Unique Value Proposition for each target audience segment to deliver it as a promise, not a slogan.
The Four Core Business Family Members are:
- Operation delivers the Unique Value Proposition for each customer segment in a Value Chain.
- Innovation creates the Unique Value Proposition for each customer segment.
- Marketing aligns the market demand of each customer segment with the Unique Value Proposition.
- Strategy creates efficiency and effectiveness by organising activities and aligning decisions to deliver the Unique Value Proposition in the market segment to generate superior economic value in a market in a form of
- Strategy as Plan (Analysis) - A set of organised and objective actions toward a desirable outcome. Critical Thinking, Analytical, logical, Linear, Rational driven, Preserve and improve the existing business model, product or service. key tools are SWOT, PESTEL, Value Chain, Five-Factors
- Strategy as Innovation (Synthesis) - Strategic Innovation is a unique change with a scalable impact on the business on purpose. Creative Thinking, Creative & disruptive, nonlinear, Passion driven, develop & experiment a new business model, product or service. Key tools are Business model canvas, Strategic Innovation Canvas, the Innovation Pyramid, Disruptive Innovation, The Play-to-Win Strategy Canvas,…
- Strategy as Pattern (Past Actions) - Strategy can emerge from a pattern in a stream of past business actions, decisions and behaviours. Rather than being an intentional choice, a consistent and successful way of doing business can develop into a strategy. Key tools are business achievement timeline, lesson-learned, 5 Ps, patterns of team success & failures, USP Analysis and Core Competence Analysis.
- Strategy as Perspective (Internal Perception) - Strategic Thinking, the strategy is formulated as per the business culture, and the way business views itself, and it's about the ‘character’ of the business to the individuals. As patterns of behaviour can emerge as strategy, patterns of thinking will shape a business' perspective and the things that it can do well. Strategy as a perspective is not just of a chosen position but of an ingrained way of perceiving the world and building internal business ideology to create a culture to respond to external demands. The business driver is internal business people mindset in taking an approach in solving problems, identify opportunities, encourages risk-taking and innovation, designing the business model and leading the operation. Key tools are the Cultural Web, Deal and Kennedy's Cultural Model, and the Congruence Model.
- Strategy as Position (External Perception) - Human Centred Thinking, defines the overall position of the business in the market. Strategic positioning establishes a focus of delivering value direction that resonates with your customers. It creates a clear position of a unique value that is different but right in the customer and consumer's minds. That's how you decide to position yourself in the marketplace and it helps you develop a sustainable competitive advantage. Key tools are PEST Analysis, Porter's Diamond, and Porter's Five Forces.
My new view of the business strategy about Marketing and Innovation is the "Strategy as Position" (Strategic Positioning).
Strategy as Position" in Who, Why, What, How, When and Where.
Who: Business Owners with businesses in thrive phase.
Why:
Strategic Positioning outcome is about to Make a sustainable and scalable business that is profitable and defendable in the market segment in contract to Market Positioning which is more about meeting a Market Position target for competitive advantage with no/weak plan to make it sustainable and scalable plan over time.
What:
“Positioning is not what you do to a product. Positioning is what you do to the mind of the prospect.” - Jack Trout and Al Ries, authors of “Positioning, The Battle For Your Mind.”
Positioning is all about creating a clear and compelling position in your customer and consumer mind, so they chose your product/service for their needs.
"Strategy should reflect a distinctive value chain that configures all key business processes and operations (operations, HRM, marketing, service delivery, etc.) in a unique way that is difficult for competitors to imitate (Porter, 2001)."
A. Strategic Positioning Vs Market Positioning
A market position (also called a “Competitive Advantage”) can be achieved through differentiated but relevant values and a distinctive operational model with Unfair competitive advantage to deliver the values (value chain) to the target market segment. However, strategic positioning is a process to continually adjust the perception of your business’s products and services in the minds of your target customers and consumers.
B. Key Strategic positioning Elements:
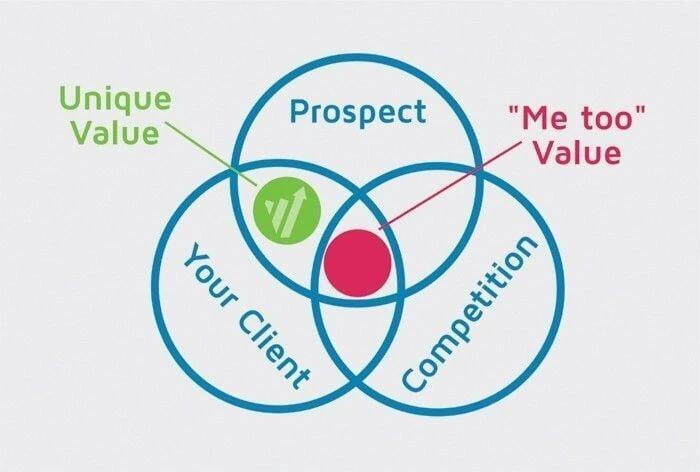
- Unique Value Proposition: The first and critical step to strategically position your business is to develop a Unique Value proposition through Innovation to set your business position different but relevant to customer's demands. By offering differentiated, relevant & distinctive value to customer's needs.
- Customers & Consumer Decision making drivers:
- People Decision Drivers in general:
- Perception: Intuitive, cognitive biases, assumptions, internal or external influence factors, imagination, personal or public beliefs,
- Facts: Analysis, Synthesis, validated data & information, comparisons, evaluation, critical judgement,
- Situation: Chaotic, Complex, Complicated and Simple situations to make a decision which is connected to the urgency in time and level of known information in a context
- Customer Decision Drivers:
- Constrains: Time, Budget, Quality, Requirements, ROI, Support, Relationship level
- Facts: Analysis, Synthesis, validated data & information, comparisons, evaluation, critical judgement,
- Unique Value Proposition bases: Make it different but right to fit a Market
- Consumer Decision Drivers:
- Perception: Intuitive, cognitive biases, assumptions, internal or external influence factors, imagination, personal or public beliefs,
- Adoption stage: Before adoption, Early adoption, late adoption, Laggards, Overuse.
- Productivity and Performance: Fast in response, Easy to use, Get things down, User for different purposes,
- Price Leadership: A premium price or lower costs for the business to stay in the market. Whether to have a lower price (not lower costs) below competitors or increasing our product/service value perception in the mind of customers and consumers. By lowering the price continually, it becomes a challenge to stay in a profitable and defensible position in a marketplace over the long run.
- Market Segments: Classify customers and split the market into segments that mostly have common characteristics that make them approachable through the same value chain.
- Target markets: Select a market segment that the business delivers the Unique Value Proposition as a promise.
C. Key Strategic positioning Principles:
- Focus on Consumer perception, not just from the customer's point of view.
- Adjusting the business market positioning accordingly as new information becomes available.
- Linking the Strategy as Position with the business operations to deliver the Unique Value Proposition as a promise.
How:
How to find and protect a “profitable” but “defensible” position in a marketplace?
Strategic Positioning Methods, Tools, Techniques;
- Value Proposition: Value Proposition Evaluation Model delivers the right value to the customer in coherence with the business capabilities.
- MORE-FOR-MORE,
- MORE-FOR-THE-SAME,
- THE-SAME-FOR-LESS,
- LESS-FOR-LESS
- LESS-FOR-MORE
- The 6 step STP model outlines the process for establishing your positioning.
- The Ansof model: The ANSOF model is a tool that demonstrates how to position your business in four given scenarios.
- Marketing Development
- Diversification
- Marketing Penetration
- Product Development
- Competitive Advantage Model
- Differentiation
- Cost leadership
- CHOOSING THE RIGHT COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
- Unique Selling Point: The types of differentiation must be:
- Important: the difference delivers high value to target buyers
- Distinctive: Competitors do not offer the difference
- Superior: it is a better way of how customers currently operate
- Communicable: is it visible and understandable by customers
- Pre-emptive: cannot be copied easily
- Affordable: buyer can afford to pay the increased costs
- Profitable: they can be implemented profitably
- Customer Journey Roadmap
- Polarising Affect: A polarising effect is a tool that you use to plan how you want to tap into the emotional state and rational state of your customers
- Position Document:
- A Positioning statement
- Positioning messages for target audiences
- Positioning for target audience via their purchasing cycle
When and Where: Usage Consideration of Strategy as Position
- Pro:
- It creates a clear position in the customer’s mind to increase the existing value of business products and services for a premium price.
- It mostly benefits businesses in thrive phase.
- It simplifies and drives strategy conversation to develop capabilities and manage systems to enable the strategy
- Focusing on business core capabilities toward market-oriented outcomes.
- Cons:
- A positioning strategy is about being different, relevant, but not necessarily better. The focus can be gradually away from continuous improvement to deliver a better product or service to satisfy dynamic customer demands or create a new set of demands without any explicit customer's needs.
- Without the right capabilities and system, the strategy is just an idea.
- Simply creating a clear position may not make you more money, it requires an effective plan and iterative process to implement it across your business value chain.
- Not for businesses in survival and revival phases.
- It is an iterative, lengthy and more likely expensive process to develop.
- Not for Me-Too type of businesses.
References:
Mintzberg's 5 Ps of Strategy
Terms reproduced from “The Strategy Concept 1: Five Ps For Strategy” by Henry Mintzberg in California Management Review, Vol. 30, 1, Fall 1987, pp. 11-24 © 1987 by the Regents of the University of California. Reprinted by permission of the University of California Press.
Sun Wu’s Strategy for Executives.
Magretta, Joan. Understanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and Strategy. Harvard Business Review Press. Kindle Edition.
Strategic Positioning, Institute for Strategic Competitiveness.
https://www.isc.hbs.edu/strategy/business-strategy/Pages/strategic-positioning.aspx
Hooley, Graham; Piercy, Nigel; Nicoulaud, Brigitte; Rudd, John M. Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning. 6th edition (Jan 2018). Pearson.
Dawar, Niraj; Bagga, Charan K. A Better Way to Map Brand Strategy. Harvard Business Review. June 2015.
https://hbr.org/2015/06/a-better-way-to-map-brand-strategy
Van Mieghem, Jan A.; Allon, Gad. Operations Strategy: Principles and Practice. Second Edition. Dynamics Ideas LLC.
https://www.kellogg.northwestern.edu/faculty/vanmieghem/books.htm#ops%20strat
https://strategyforexecs.com/strategic-positioning/
https://allbusinesstoolkit.com/strategic-positioning/
https://strategyforexecs.com/strategic-positioning/
https://medium.com/swlh/positioning-5-strategies-to-stand-out-from-your-competitors-bb3ba93e4a69